Navigating the complexities of NY income tax can be daunting for residents, especially those unfamiliar with the state's unique tax laws and regulations. As one of the most tax-heavy states in the nation, New York demands a thorough understanding of its income tax system to ensure compliance and optimize financial planning. Whether you're a long-time resident or a newcomer, staying informed about NY income tax rates, filing requirements, and potential deductions is essential for managing your finances effectively.
With ever-changing tax laws and increasing scrutiny from the IRS and state authorities, it's crucial to remain updated on the latest developments in NY income tax policies. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the key aspects of New York's income tax system, offering practical advice and insights to help you make informed decisions. From understanding the tax brackets to exploring available deductions, we'll cover everything you need to know to simplify your tax obligations.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we'll explore common questions and concerns related to NY income tax, providing actionable tips to help you navigate the complexities. Whether you're self-employed, work for a company, or have multiple sources of income, understanding the intricacies of New York's tax system can lead to significant savings and peace of mind. Let's get started by outlining the key areas we'll cover in this guide.
Read also:Unveiling The Mystique A Comprehensive Guide To Skz
Table of Contents
- What Are the NY Income Tax Rates?
- How Do I File My NY Income Tax?
- NY Income Tax: What Are the Deductions Available?
- Can I Appeal My NY Income Tax Assessment?
- Overview of NY Income Tax Brackets
- Understanding Tax Obligations
- Key Considerations for Self-Employed Individuals
- Exploring Tax Credits in NY
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Resources for Further Assistance
What Are the NY Income Tax Rates?
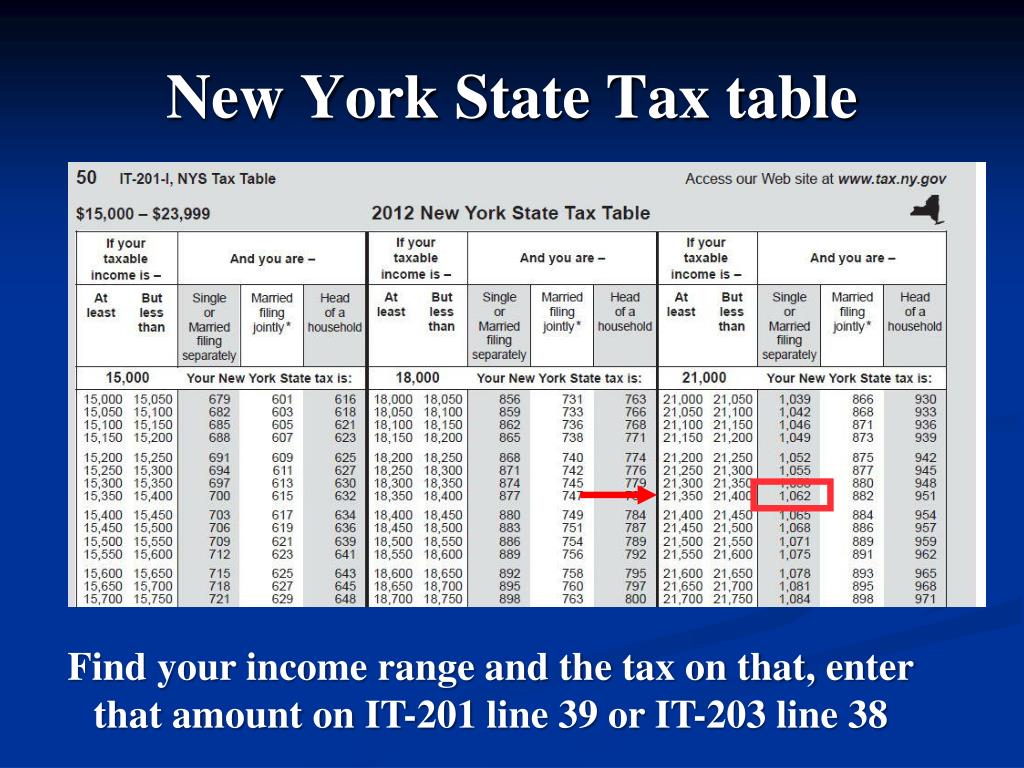
NY income tax rates vary depending on your income level and filing status. As of the latest updates, New York uses a progressive tax system with multiple brackets designed to ensure fairness across different income levels. For individuals earning lower incomes, the tax rate starts at a relatively low percentage, gradually increasing as income rises. This structure aims to balance the financial burden on taxpayers while generating sufficient revenue for state services.
For example, single filers earning under $8,500 pay a tax rate of 4%, while those in higher brackets, such as $215,400 or more, face a top rate of 8.82%. It's important to note that these rates are subject to change, so staying informed about legislative updates is crucial for accurate tax planning. Additionally, married couples filing jointly may benefit from slightly different thresholds, offering potential savings for those who qualify.
How Do I File My NY Income Tax?
Filing your NY income tax can be done through several methods, including online submission via the Department of Taxation and Finance website or traditional paper forms. Many residents opt for electronic filing due to its convenience and faster processing times. To ensure a smooth filing process, gather all necessary documents beforehand, such as W-2s, 1099s, and any applicable deduction or credit forms.
When filing, pay close attention to deadlines to avoid penalties. The standard deadline aligns with federal tax deadlines, typically April 15th, unless extensions are granted. If you anticipate owing taxes, consider making estimated payments throughout the year to minimize your liability at tax time. For those who qualify, extensions can provide additional time to file without incurring late fees, though any owed taxes must still be paid by the original deadline.
NY Income Tax: What Are the Deductions Available?
A key aspect of managing NY income tax efficiently involves leveraging available deductions. New York offers a variety of deductions designed to reduce taxable income, ultimately lowering your overall tax burden. Common deductions include contributions to retirement accounts, mortgage interest payments, and certain business expenses for self-employed individuals.
Additionally, residents may qualify for deductions related to dependent care expenses, educational costs, and medical expenses exceeding a certain percentage of income. To maximize your deductions, keep detailed records throughout the year and consult with a tax professional if you're unsure about eligibility. Proper documentation is critical for claiming deductions accurately and avoiding potential audits.
Read also:Unveiling The Timeless Romance John Denver And Annie Martell
Can I Appeal My NY Income Tax Assessment?
If you believe your NY income tax assessment is incorrect or unfair, you have the right to appeal the decision. The appeals process involves submitting a formal request to the Department of Taxation and Finance, providing evidence to support your case. Common reasons for appealing include discrepancies in income reporting, incorrect deductions, or miscalculated tax liabilities.
When filing an appeal, ensure all documentation is complete and organized, clearly outlining the basis for your disagreement. It's often beneficial to seek legal counsel or consult a tax professional to strengthen your case and navigate the complexities of the appeals process. Appeals can take time to resolve, so patience and persistence are key to achieving a favorable outcome.
Overview of NY Income Tax Brackets
Understanding NY income tax brackets is fundamental to estimating your tax liability accurately. The state divides taxpayers into distinct brackets based on income levels, applying different rates to each portion of earnings. For instance, the first $8,500 of income might be taxed at 4%, while income exceeding $215,400 could be taxed at the highest bracket of 8.82%.
These brackets are designed to ensure that higher earners contribute proportionally more to state revenues, while lower-income individuals face a lighter tax burden. By familiarizing yourself with the applicable brackets, you can better anticipate your tax obligations and plan accordingly. Keep in mind that adjustments to these brackets occur periodically, so staying informed is essential for accurate tax calculations.
Key Considerations for Self-Employed Individuals
Self-employed individuals face unique challenges when managing NY income tax, as they are responsible for both personal and business-related tax obligations. Unlike traditional employees, self-employed residents must account for self-employment taxes in addition to standard income tax. This dual responsibility can significantly increase the overall tax burden, making careful planning even more critical.
To mitigate these challenges, self-employed individuals should take advantage of available deductions, such as home office expenses, travel costs, and business-related supplies. Keeping meticulous records of all business transactions and expenses is crucial for accurate reporting and maximizing deductions. Additionally, setting aside a portion of earnings throughout the year for estimated tax payments can help avoid unexpected liabilities at tax time.
Understanding Tax Obligations
Beyond income tax, New York residents must also consider other tax obligations that may impact their overall financial picture. Property taxes, sales taxes, and excise taxes all contribute to the state's revenue streams, potentially affecting disposable income. While these taxes are separate from NY income tax, they should be factored into comprehensive financial planning to ensure a complete understanding of your tax responsibilities.
For instance, homeowners must budget for annual property tax payments, which vary based on location and property value. Similarly, sales taxes affect everyday purchases, adding to the overall cost of goods and services. By incorporating these additional taxes into your planning, you can create a more accurate financial forecast and make informed decisions about spending and saving.
Exploring Tax Credits in NY
In addition to deductions, New York offers various tax credits to help reduce the overall tax burden for eligible residents. Tax credits differ from deductions in that they directly reduce the amount of tax owed, rather than just lowering taxable income. Popular credits include the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), Child Tax Credit, and credits for education-related expenses.
To qualify for these credits, taxpayers must meet specific criteria, often based on income levels, family size, or specific expenses. For example, the EITC is designed to assist low- to moderate-income working individuals and families, providing substantial relief for those who qualify. Exploring available credits and ensuring eligibility can lead to significant savings and improved financial well-being.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When dealing with NY income tax, avoiding common mistakes is crucial for maintaining compliance and minimizing potential penalties. One frequent error involves failing to report all sources of income, whether from employment, investments, or side gigs. Underreporting income can lead to audits and substantial fines, so thorough documentation is essential.
Another common pitfall is missing deadlines for filing or paying taxes. Late filings or payments can result in interest charges and penalties, compounding the financial burden. To avoid these issues, set reminders for key dates and consider using tax preparation software or consulting a professional to ensure accuracy and timeliness. Additionally, neglecting to claim available deductions or credits can leave money on the table, so always review your eligibility carefully.
Resources for Further Assistance
For residents seeking additional guidance on NY income tax matters, numerous resources are available to provide support and clarification. The New York State Department of Taxation and Finance offers extensive online resources, including FAQs, forms, and calculators to assist with tax-related questions. Tax professionals, such as CPAs and enrolled agents, can offer personalized advice tailored to your specific situation, ensuring compliance and optimizing savings.
Community organizations and non-profits may also provide free or low-cost tax assistance, particularly for low-income individuals or seniors. Taking advantage of these resources can enhance your understanding of NY income tax requirements and improve your ability to manage your financial obligations effectively. Remember, staying informed and proactive is the key to navigating the complexities of New York's tax system successfully.